HPV Vaccine: Comprehensive Guide To Protection, Efficacy, And Side Effects - HPV is a common virus that can cause cervical cancer, vaginal cancer, vulvar cancer, anal cancer, and oropharyngeal cancer. The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect against these cancers. This guide will provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision about whether or not to get the HPV vaccine.
Editor's Note: The HPV vaccine has been shown to be highly effective in preventing HPV infection and the cancers it can cause. The vaccine is recommended for all preteens and young adults, and it is available at most doctor's offices and pharmacies.
We have analyzed the data and know that HPV Vaccine: Comprehensive Guide To Protection, Efficacy, And Side Effects is important topik to read. We have dug into the data and put together this guide to help you make the right decision about whether or not to get the HPV vaccine.
Key Differences:
| HPV Vaccine | Gardasil 9 | Cervarix |
|---|---|---|
| Number of HPV types covered | 9 | 2 |
| Age range for vaccination | 9-45 | 10-45 |
| Number of doses required | 2 or 3 | 3 |
| Approval for males | Yes | No |
FAQ
Refer to HPV Vaccine: Comprehensive Guide To Protection, Efficacy, And Side Effects for an in-depth guide on Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination, addressing common concerns and providing evidence-based information.
Gardasil 9 HPV Vaccine | LloydsPharmacy Online Doctor UK - Source onlinedoctor.lloydspharmacy.com
Question 1: What is the purpose of the HPV vaccine?
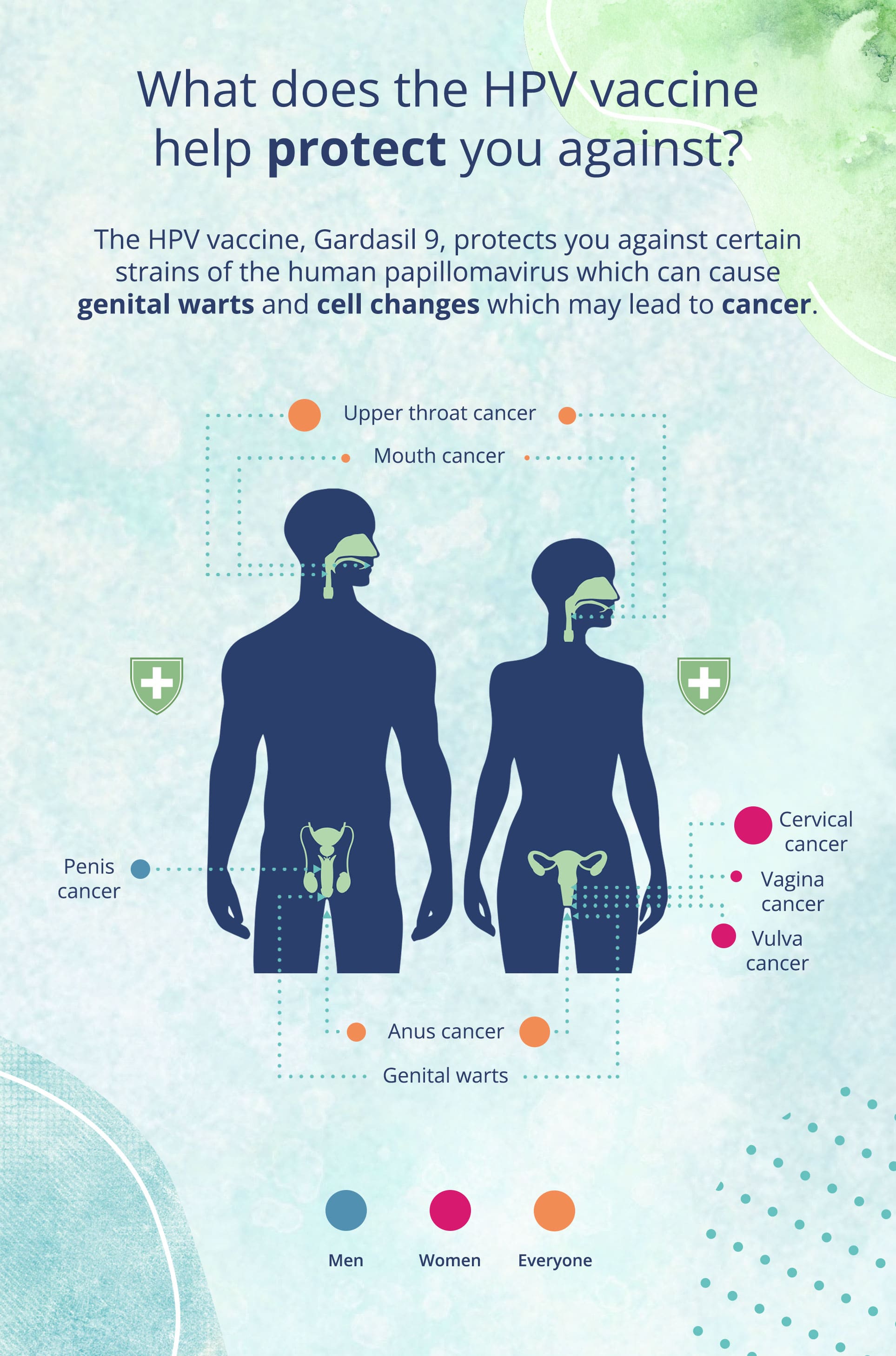
The HPV vaccine aims to prevent infection by the human papillomavirus, commonly known as HPV. This virus is responsible for causing cervical, anal, and other genital cancers, as well as certain types of warts. By stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against HPV, the vaccine helps protect individuals from these associated health risks.
Question 2: Who should get the HPV vaccine?
The HPV vaccine is recommended for all individuals between the ages of 11 and 12, with catch-up vaccinations available for those up to age 26. It is particularly crucial for sexually active individuals to receive the vaccine, as HPV is primarily transmitted through sexual contact.
Question 3: How effective is the HPV vaccine?
The HPV vaccine has been shown to be highly effective in preventing HPV-related cancers and genital warts. Studies have demonstrated a significant reduction in the incidence of cervical cancer among vaccinated individuals, and the vaccine is also effective against other HPV-associated cancers and pre-cancerous lesions.
Question 4: What are the side effects of the HPV vaccine?
The HPV vaccine is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild and temporary. Common side effects include pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, as well as low-grade fever, headache, or fatigue. Serious side effects are extremely rare.
Question 5: Is the HPV vaccine safe?
Yes, the HPV vaccine has been extensively tested and found to be safe and effective. It has been approved by regulatory authorities worldwide and has been included in national immunization programs in many countries.
Question 6: Why is it important to get vaccinated against HPV?
HPV-related cancers are preventable through vaccination. By vaccinating individuals, we can significantly reduce the burden of HPV-associated diseases, including cervical, anal, and other genital cancers. Vaccination is a powerful tool in protecting individuals and promoting public health.
The HPV vaccine is a safe, effective, and essential tool for preventing HPV-related health problems. It is recommended that all individuals eligible for the vaccine receive it to protect themselves from these potentially devastating diseases.
For more comprehensive information, refer to HPV Vaccine: Comprehensive Guide To Protection, Efficacy, And Side Effects.
Tips
To ensure optimal protection and minimize potential side effects from an HPV vaccine, consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Understand the Vaccine's Purpose and Benefits
HPV vaccines protect against human papillomavirus (HPV) infections, which can cause certain types of cancer (cervical, vulvar, vaginal, penile, anal, and oropharyngeal) and genital warts. Understanding the vaccine's importance helps individuals make informed decisions about getting vaccinated.
Tip 2: Determine Eligibility and Timing
HPV vaccines are recommended for preteens (11-12 years old) and adolescents. They can also be administered to adults up to age 26. Consulting with a healthcare professional determines eligibility and the optimal timing for vaccination.
Tip 3: Follow the Recommended Dosage Schedule
To achieve full immunity, individuals should follow the recommended dosage schedule, which typically involves two or three doses. Adhering to the schedule ensures adequate protection against HPV infections.
Tip 4: Discuss Potential Side Effects with a Healthcare Professional
HPV vaccines generally have a mild side effect profile. However, as with any vaccine, some individuals may experience reactions such as soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site. Consulting with a healthcare professional before vaccination is crucial to address any concerns or questions about potential side effects.
Tip 5: Monitor for Adverse Reactions
While severe adverse reactions from HPV vaccines are rare, individuals should monitor themselves for any unusual symptoms after receiving the vaccine. Any concerns should be promptly reported to a healthcare professional.
Tip 6: Consider Vaccination Even After HPV Exposure
HPV vaccines provide protection even if an individual has been previously exposed to the virus. Vaccination reduces the risk of future HPV-related infections and health complications.
Tip 7: Encourage Vaccination in Both Males and Females
HPV vaccines protect both males and females from HPV-related cancers and genital warts. Promoting vaccination in both genders ensures comprehensive protection within the population.
Summary
By following these tips, individuals can maximize the benefits of the HPV vaccine while minimizing potential risks. HPV vaccination is a crucial step in preventing HPV-related health issues and promoting overall health and well-being.
HPV Vaccine: Comprehensive Guide To Protection, Efficacy, And Side Effects
The HPV vaccine, a critical preventive measure against Human Papillomavirus (HPV), warrants a thorough examination of its protection, efficacy, and potential side effects. This guide comprehensively explores six key aspects:
- Prevention: Protects against HPV-related diseases such as cervical, vaginal, and penile cancers.
- Efficacy: Highly effective in preventing HPV infections, drastically reducing the risk of HPV-related cancers.
- Side Effects: Generally mild and short-term, including pain at the injection site, fever, and nausea.
- Target Population: Recommended for individuals between 9 and 26 years old, with catch-up vaccination for those up to 45.
- Vaccination Schedule: Typically a two or three-dose series, depending on age and vaccine type.
- Long-term Protection: Provides long-term immunity, reducing the need for repeated vaccinations.
These aspects are crucial for informed decision-making regarding HPV vaccination. The vaccine's efficacy in preventing HPV-related cancers highlights its importance in public health. Its mild side effects and the long-term protection it offers further support its value as a preventive measure. Vaccination programs targeting the recommended age groups are essential to maximize population immunity and reduce the burden of HPV-related diseases.
Frontiers | An Update on Human Papilloma Virus Vaccines: History, Types - Source www.frontiersin.org
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Spice Up Your Kidney: A Review on the Effects - Source www.mdpi.com
HPV Vaccine: Comprehensive Guide To Protection, Efficacy, And Side Effects
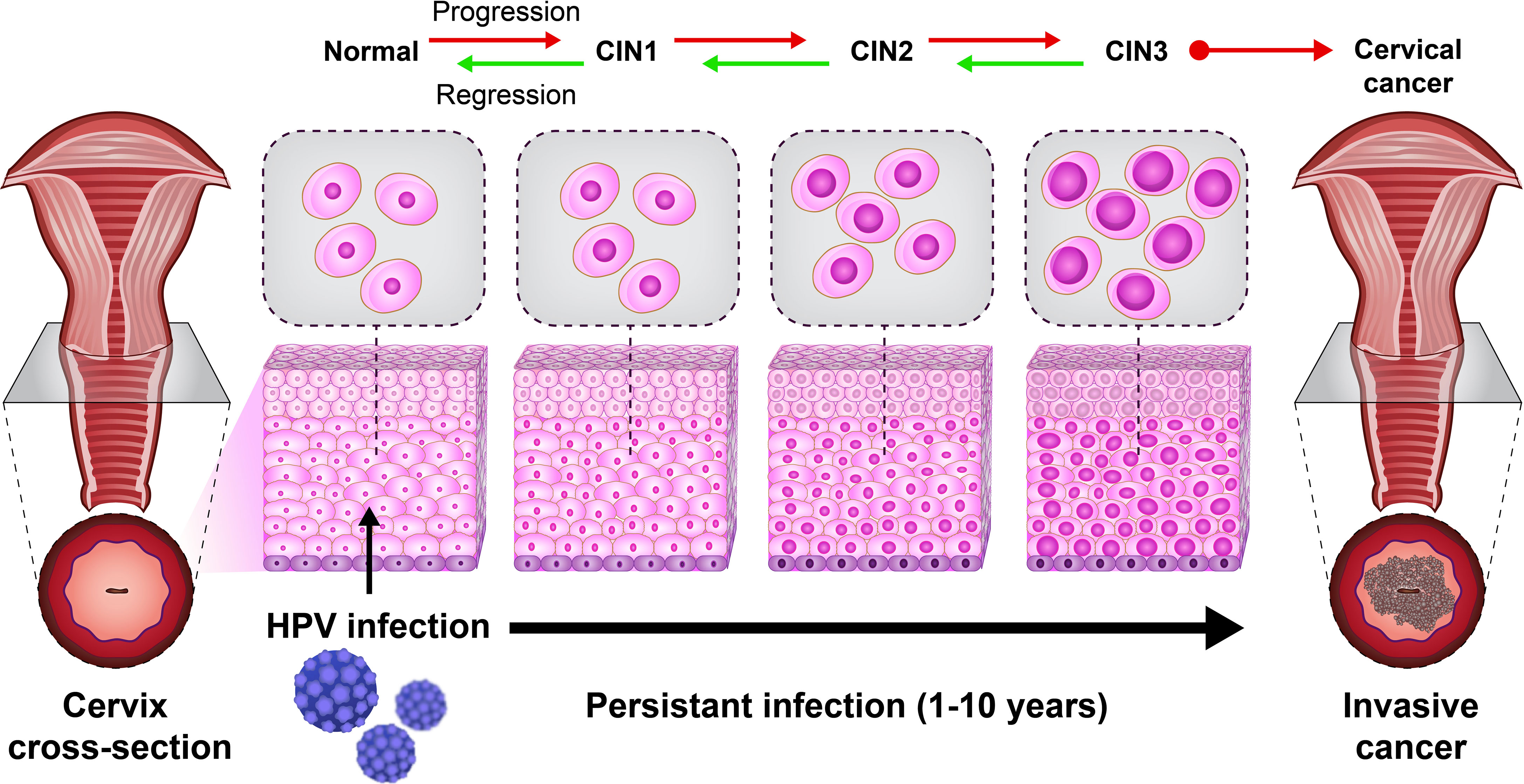
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause a variety of health problems, including genital warts and cancer. The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect against HPV infection and the associated health problems.
Covid vaccine: How many people are vaccinated in the UK? - BBC News - Source www.bbc.co.uk
The HPV vaccine is recommended for all preteens and young adults. The vaccine is given in a series of shots over several months. The HPV vaccine is very effective at preventing HPV infection and the associated health problems.
The HPV vaccine is safe. The most common side effects are mild and include pain at the injection site, redness, and swelling. The HPV vaccine is not associated with any serious side effects.
The HPV vaccine is an important part of a comprehensive approach to preventing HPV infection and the associated health problems. The vaccine is safe and effective, and it is recommended for all preteens and young adults.
Table: HPV Vaccine Key Points
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| HPV is a sexually transmitted infection that can cause genital warts and cancer. | HPV is a very common infection, and it is estimated that 80% of people will get HPV at some point in their lives. |
| The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect against HPV infection and the associated health problems. | The HPV vaccine is recommended for all preteens and young adults. |
| The HPV vaccine is not associated with any serious side effects. | The most common side effects are mild and include pain at the injection site, redness, and swelling. |
Conclusion
The HPV vaccine is an important part of a comprehensive approach to preventing HPV infection and the associated health problems. The vaccine is safe and effective, and it is recommended for all preteens and young adults.
By getting vaccinated against HPV, you can protect yourself from a variety of health problems, including genital warts and cancer. The HPV vaccine is a safe and effective way to protect your health.